Governance
Governance
The purpose of governance is to make sure the application always provides what the business needs and covers the entire lifecycle.Agile Project management Change management Requirements management
Governance refers to the process of defining, implementing, and enforcing policies and procedures for managing software development and deployment activities. In both Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) and DevOps, governance is an important aspect that ensures that the software development process is efficient, effective, and compliant with relevant regulations and standards.
In ALM, governance involves creating and enforcing policies and procedures for managing the software development lifecycle. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing development standards and practices, and ensuring that software development activities are aligned with business goals and objectives. ALM governance also involves managing risks and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
In DevOps, governance involves defining policies and procedures for managing the entire software development and deployment pipeline. This includes defining standards for version control, automated testing, continuous integration and deployment, and security. DevOps governance also involves monitoring and measuring performance metrics, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
Overall, governance is critical to the success of software development and deployment activities in both ALM and DevOps. Effective governance ensures that software development activities are aligned with business goals and objectives, risks are managed effectively, and compliance with relevant regulations and standards is maintained.
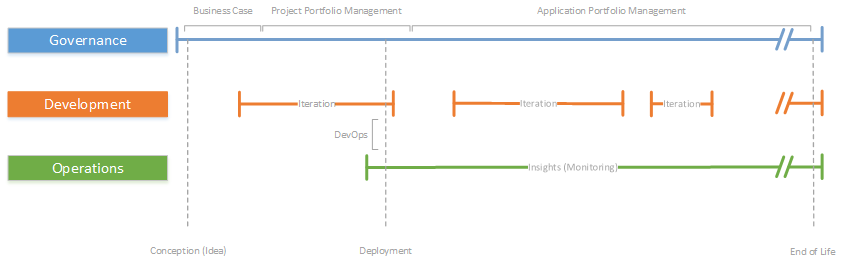
Typically the life of an application starts with a business case that’s been developed using Business Case Development (BCD) methodologies. Many organizations are using Project Management methodologies to transform the business case to a real application and Project Portfolio Management. When the first initial release is deployed into production the application responsibility typically move from the Project Portfolio Management (PPM) to the Application portfolio Management (APM).
ALM governance focus the discipline of IT asset management of software assets and this process becomes increasingly important as organization grow, mature and collect more software assets.
ALM provides effective processes and guidelines for onboarding new technologies and applications as well as retiring those that have served their purpose.
Most business processes undergo constant re-evaluation, but most deployed applications don’t, making the application remain fixed while the business process change around them. ALM Governance cover the entire lifecycle and continually re-evaluate insights.
- BPM (Business Process Management)
Lean/Agile Governance
- Product Ownership
What is Lean IT Governance?
Lean IT Governance is the leadership, organizational structures and streamlined processes to enable IT to work as a partner in sustaining and extending the organization’s ability to produce meaningful value for its customer
Source: disciplinedagiledelivery
Strategy
## ToDo ##
- Roadmap
- E-Strategy
- Strategies
- Digital strategy
- IT strategy
- Cloud Strategy
Enterprise/Business Architecture
Cutomer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Portfolio Management
Microsoft Cloud Governance
Disciplines
- Business Case Development
- Application Portfolio Management
- Assets Management
- Security Management
- License Management
- (Enterprise Architecture)
Links
## ToDo ##
- AI & Machine learning
- Application portfolio management
- Business case management
- Decision support
- Digital Project Management
- Lean Management
- Quality Management
- Six Sigma
- Technology mapping (POC labs) [R&D]
- AI Development Platforms
- AI Infrastructure
- Anomaly Detection Tools
- Applicant Tracking and Recruiting Software
- Appointment Scheduling Software
- Benefits Administration
- BI and Performance Management Service Providers
- BI Tools
- Business Activity Monitoring
- Business Management Software
- Business Performance Management
- Business Process Design
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Business Rules Management
- Chatbot Development Platforms
- Cloud Email
- Cloud ERP
- Cloud HCM
- Community Platforms
- Content Collaboration Platforms
- Continuous Controls Monitoring
- Data Mining
- Data Privacy Management Software
- Data Science Platforms
- Data Visualization
- Decision Management Tools
- Digital Adoption Platforms
- Digital Signage Software
- DMARC Authentication Software
- Document Automation Software
- Document Generation Tools
- Document Management Software
- eLearning
- Electronic Document Delivery
- Email Applications
- Email Archiving
- Email Security
- Email Signature Software
- Embedded BI Tools
- Employee Scheduling Software
- Employee Time Tracking Software
- Enterprise Content Management
- Enterprise Intranet
- Enterprise Social Software
- ERP
- Fax Software
- Digital Forensics Platforms
- Local Government CRM
- Form Management
- Global Payroll
- Grant Management Software
- GRC
- HR Analytics Software
- HRO
- Innovation Management Software
- Intellectual Property Management
- Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
- Learning Management Systems
- Location Intelligence Platforms
- Low-Code Development Platforms
- Managed Collaboration Services
- Microsoft Dynamics Service Providers
- Mind Mapping Software
- No-Code Development Platforms
- Office 365 Protection
- Oracle Applications Service Providers
- Order-to-Cash BPO Providers
- Pre-Employment Testing Software
- Predictive Analytics
- Process Automation
- Process Mining
- Quality Management Software
- Reporting Tools
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- SAP Service Providers
- Shared Inbox
- Speech-To-Text Services
- Talent Acquisition
- Talent Intelligence
- Talent Management
- Text-To-Speech Services
- Translation Management Software
- Video Interviewing Software
- Virtual Events Platforms
- Virtual IT Labs
- Virtual Meetings
- Virtual Training
- Visual Collaboration Platforms
- Web Content Management
- Website Accessibility Testing Software
- Wireless Email