Citizen Development
Citizen development is a business trend that encourages employees to experiment with low-code no-code software development platforms.
Citizen development is a disruptive approach to digital transformation and organizational innovation, where teams are empowered to turn ideas into applications using no-code/low-code technology.
- CitDev or CD for short
What is Citizen Development?
Citizen Development is a rapidly growing movement within the tech and business sectors that empowers non-technical individuals to create applications and solutions through intuitive development platforms, often without the need for extensive coding knowledge. This approach promotes innovation and efficiency by enabling everyday users, such as business analysts and other professionals, to actively participate in the software development process.Key aspects of Citizen Development include:
- Empowerment: Allows non-developers to design, build, and implement applications that meet their specific needs.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Utilizes tools that simplify application development, providing drag-and-drop features and visual interfaces.
- Collaboration: Fosters teamwork between IT departments and business units, enhancing communication and alignment on project objectives.
- Agility: Accelerates the development process, allowing organizations to quickly adapt to changing business demands.
- Innovation: Encourages creative solutions, as users can experiment and iterate on applications with less risk.
By leveraging citizen development, organizations aim to balance the demand for software solutions with the available technical resources, ultimately driving digital transformation and business agility.
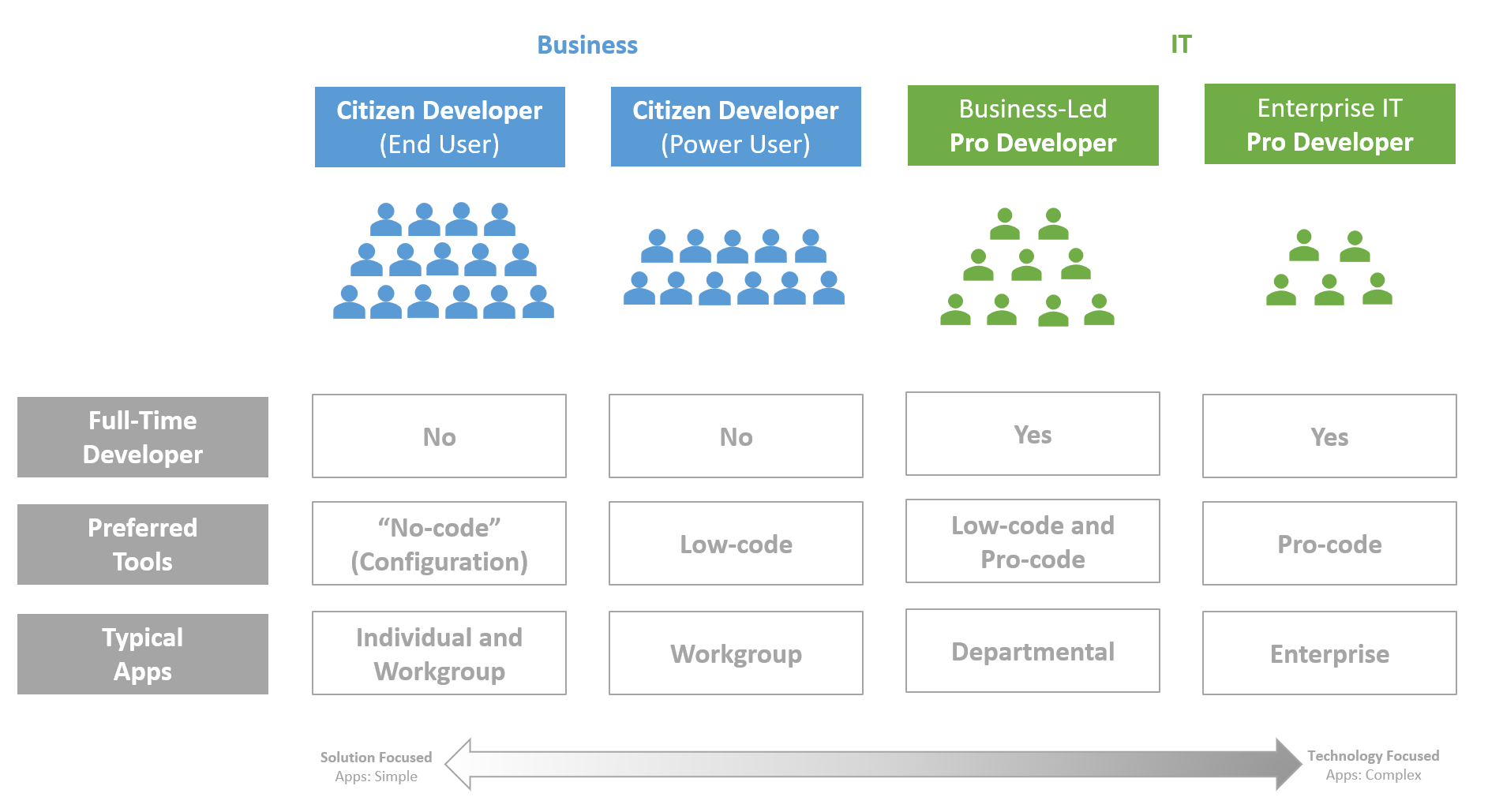
What is Citizen Developer?
A citizen developer is a user who creates new business applications for consumption by others using development and runtime environments sanctioned by corporate IT. In the past, end-user application development has typically been limited to single-user or workgroup solutions built with tools like Microsoft Excel and Access. However, today, end users can build departmental, enterprise and even public applications using shared services, fourth-generation language (4GL)-style development platforms and cloud computing services.— Gartner
The greatest enabler of change of a generation.
The democratisation of software development and delivery means the world can now create meaningful applications without any coding experience.
Low-code and no-code platforms are smarter than ever and sophisticated enough to generate code based on visual inputs and diagrams.
Technology is now more accessible which has empowered new consumer groups to create value. The rise of Citizen Developer.
Citizen development is the practice of allowing non-technical or business users to create software applications using low-code or no-code platforms. Citizen development has become increasingly popular in recent years due to the growing demand for customized software applications that meet specific business needs.
In Application Lifecycle Management (ALM), Citizen Development can play a role in the design and development phases. By enabling non-technical or business users to create and modify software applications, ALM teams can better align software development activities with business needs and objectives. This can lead to faster and more effective software development, as well as increased collaboration and communication between business users and technical teams.
In DevOps, Citizen Development can be integrated into the continuous delivery pipeline, enabling business users to create and deploy software applications directly into production environments. This can help to accelerate software delivery and improve collaboration between business users and technical teams. However, it is important to ensure that proper governance and security measures are in place to mitigate the risks associated with citizen development, such as data privacy and security concerns.
Overall, Citizen Development can be a valuable component of both ALM and DevOps, enabling business users to contribute to the software development process and align software applications with business needs and objectives. However, it is important to ensure that proper governance and security measures are in place to ensure the quality and security of software applications developed by non-technical or business users.
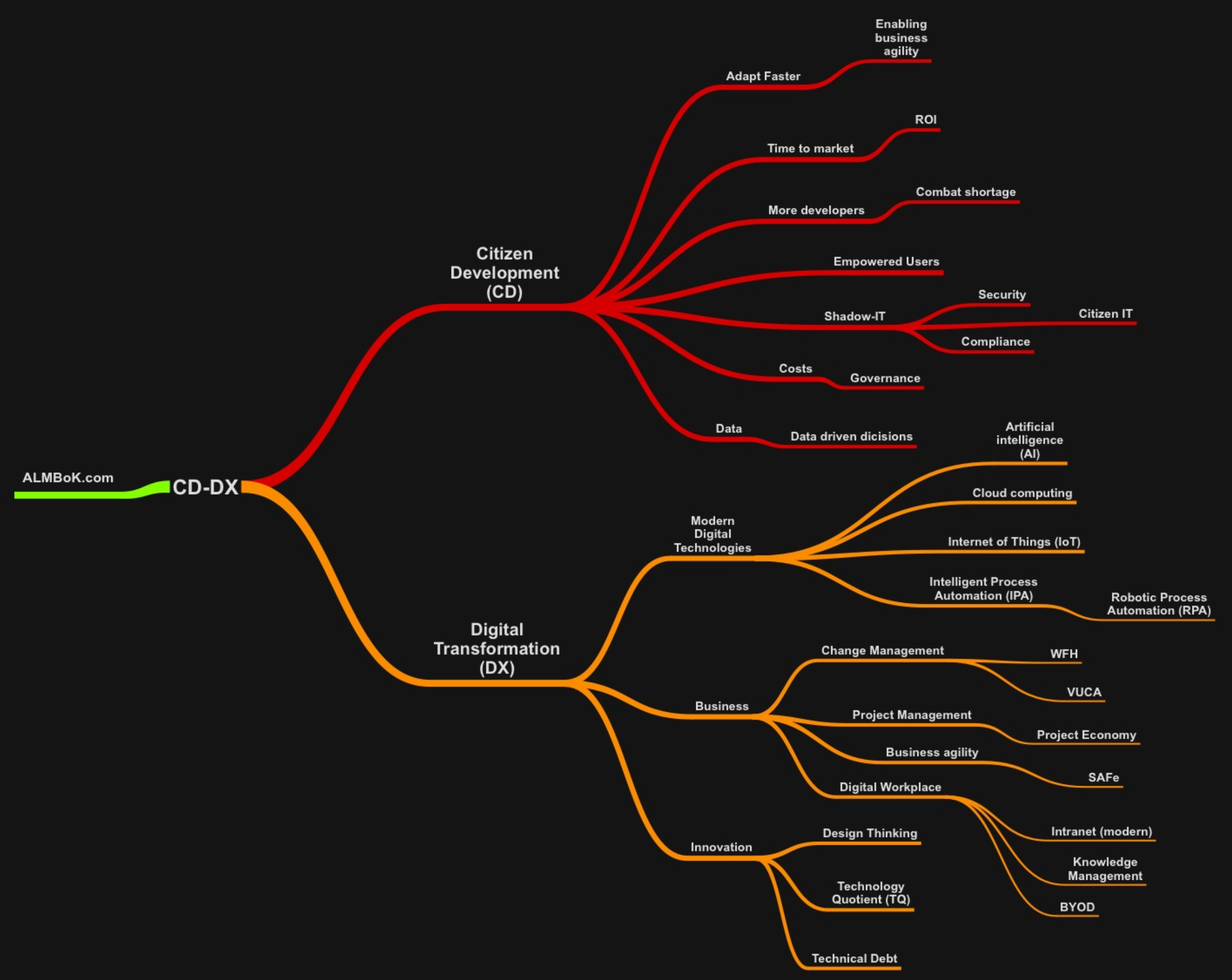
Benefits of Citizen Development
- Adapt Faster - Enabling business agility and resilience
- Time to market - Delivery speed, respond to change quickly
- More Resources - Shortage of Developers
- Empowered Users - Empowers business leaders and end users to create their own solutions
- Compliance and security - Convert Shadow-IT to Citizen-IT and ensure Business-IT alignment
- Costs - Reduced app development costs
- Data - Data driven decisions
- Increased Agility: Citizen development allows organizations to quickly develop and deploy software applications to meet specific business needs. This can help organizations to be more responsive to changing business requirements and customer needs, and to quickly adapt to new market conditions.
- Increased Collaboration: Citizen development can help to bridge the gap between business users and IT teams, fostering collaboration and communication between these groups. By involving business users in the software development process, organizations can ensure that software applications are aligned with business needs and objectives.
- Reduced Cost: Citizen development can be a cost-effective way to develop software applications, as it enables organizations to leverage existing resources and expertise within the organization. By allowing non-technical or business users to develop software applications, organizations can reduce their reliance on expensive external consultants or software development vendors.
- Improved Innovation: Citizen development can help to unlock new ideas and innovation within the organization, as non-technical or business users bring their unique perspectives and experiences to the software development process. This can lead to the development of new and innovative software applications that help organizations to differentiate themselves from their competitors.
- Increased Productivity: Citizen development can help to increase productivity by enabling non-technical or business users to automate manual processes and tasks, freeing up time for other high-value activities. By automating routine tasks and processes, organizations can improve efficiency and reduce errors and delays.
- Reduced Backlog: Citizen development can help to reduce the backlog of software development projects, as non-technical or business users can develop simple software applications or automations without relying on IT teams. This can free up IT resources to work on more complex or strategic projects.
- Better User Experience: Citizen developers often have a better understanding of the end-user needs and preferences, which can result in software applications that are more user-friendly and intuitive. This can lead to increased user adoption and satisfaction.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Citizen development can help organizations to speed up their time-to-market for software applications, as non-technical or business users can develop and deploy applications more quickly than IT teams. This can be especially valuable for organizations operating in fast-moving industries or with rapidly changing customer needs.
- Improved Process Efficiency: Citizen development can help to improve process efficiency by automating routine tasks and processes. By streamlining processes and reducing manual intervention, organizations can reduce errors and delays, as well as improve process consistency and quality.
Overall, Citizen Development can be a valuable tool for organizations looking to develop software applications that meet specific business needs, while also fostering collaboration, innovation, and cost-effectiveness.
However, it is important to ensure that proper governance and oversight mechanisms are in place to mitigate the risks associated with Citizen Development.
Real value achieved through Citizen Development
Examples of real value that organizations have achieved through Citizen development:
- Improved Sales Operations: A global manufacturing company used citizen development to develop a custom CRM system that integrated with their existing ERP system. The CRM system enabled sales teams to track customer interactions, leads, and opportunities more effectively, which resulted in a 10% increase in sales productivity and a 15% increase in revenue.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: A large retail bank used citizen development to develop a mobile banking app that enabled customers to access their accounts, transfer funds, and pay bills more easily. The app was developed in collaboration with a group of business users and resulted in a 30% increase in customer engagement and a 20% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Streamlined Business Processes: A healthcare provider used citizen development to develop a custom application for tracking patient referrals and appointments. The application enabled clinical staff to manage patient referrals and appointments more efficiently, reducing wait times for patients by 50% and increasing patient satisfaction scores by 15%.
- Increased Employee Productivity: A global energy company used citizen development to develop a suite of custom automation tools for their finance and accounting teams. The automation tools enabled non-technical users to automate routine tasks such as data entry, reconciliation, and reporting, which resulted in a 40% increase in team productivity and a 25% reduction in errors.
- Accelerated Innovation: A large technology company used citizen development to run an internal innovation challenge that invited employees from across the organization to submit ideas for new software applications or business processes. The challenge resulted in the development of several innovative applications, including a custom project management tool and a virtual assistant for HR inquiries, which helped to improve overall organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
By leveraging the creativity, expertise, and perspectives of non-technical or business users, organizations can develop software applications that meet specific business needs, while also improving agility, innovation, productivity, and user experience.
Citizen development is the practice of allowing employees who are not professional developers to create or customize applications to support their work using low-code or no-code tools.
Citizen development can help to increase the speed of application development, improve employee engagement and satisfaction, reduce IT backlog, and promote innovation within an organization.
Low-code and no-code platforms are software development tools that allow users to create and deploy applications with little to no coding knowledge or experience. These platforms use visual interfaces and pre-built components to simplify the application development process.
Citizen development requires skills such as problem-solving, creativity, and communication. While coding knowledge is not always necessary, users should have a basic understanding of logic and algorithms.
Citizen development can be used to create a wide range of applications, including simple productivity tools, data dashboards, and custom workflows. It can also be used to integrate existing systems and automate business processes.
Some common challenges associated with citizen development include maintaining security and compliance standards, ensuring the scalability and reliability of applications, and managing the quality of code.
Organizations can encourage and support citizen development by providing training and resources, establishing governance frameworks and standards, and fostering a culture of innovation and experimentation.
IT plays an important role in citizen development by providing guidance and support to citizen developers, ensuring compliance with organizational policies and standards, and providing technical infrastructure and resources.
Citizen development is often seen as a key component of digital transformation, as it enables organizations to quickly create and deploy applications to support their digital initiatives. It can also help to democratize innovation and promote a culture of continuous improvement.
Examples of successful citizen development initiatives include applications developed by employees at companies like Toyota, Caterpillar, and Honeywell, as well as citizen development programs implemented by government agencies to improve citizen services.
- Alternative names to Citizen Development.txt
* Low-code development * No-code development * Rapid application development * End-user development * Business-led development * Ad hoc development * Agile development * Agile innovation * Autonomous development * Bottom-up development * Business process automation * Citizen programming * Citizen-centric development * Collaborative development * Collaborative innovation * Crowd-sourced development * Decentralized development * Departmental development * DIY (Do-It-Yourself) development * DIY innovation * End-user innovation * Grassroots development * Grassroots innovation * In-house development * Lightweight development * Non-technical development * Participatory development * Self-directed development * Self-help development * Self-made development * Self-made innovation * Self-organized development * Self-service development * Shadow IT (Mitigation Development) * User innovation * User-developed solutions * User-driven development * User-driven innovation * User-generated development * User-initiated development
To accelerate this, we must enable a new category of developers — Citizen Developers — equipping domain experts with tools that are low-code or no-code to create solutions that solve their unique business needs and help them better collaborate with professional developers. With Power Platform, anyone can become a citizen developer, able to create an application, build a virtual agent, automate a workflow, and analyze data in hours or days, not weeks or months.
— Satya Nadella, CEO at Microsoft
But 86% of IT decision-makers say the biggest challenge to digitally transform their business is too few software developers.
— PMI Citizen Developer
Citizen Development Platform Analysis
PMI - Citizen Development
Related:
External links:
- Governing Citizen Development A strategy…
- 7 Benefits of Implementing Citizen Development — kissflow.com
- Speed and Agility
- Enhanced Innovation
- Align App Design with User Needs
- Increases Efficiency
- Optimized Costs
- Reduced Burden on IT
- Increased Transparency
-
- Citizen development has become a transformative approach in the modern workplace, enabling non-technical employees to create applications and automate processes. Microsoft's Power Platform is a key enabler of this trend, providing tools like Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Virtual Ag
Related:
## ToDo ##
- Support Us... →
- Service-now
- Salesforce - https://www.salesforcecitizendevelopment.com/
- Low-code and No-code Platforms
- Citizen Developer Tools and Frameworks
- Rapid Application Development (RAD)
- Workflow Automation
- Collaboration and Social Technologies
- User-Centered Design and User Experience (UX)
- Integration with Legacy Systems
- Data Management and Governance
- Security and Compliance
- Training and Support for Citizen Developers
- Citizen Development Communities and User Groups
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Custom Applications for Business and Productivity
- Digital Transformation and Innovation
- Agile and DevOps for Citizen Development
- Citizen Development and the Future of Work
- Citizen Development and IT Governance